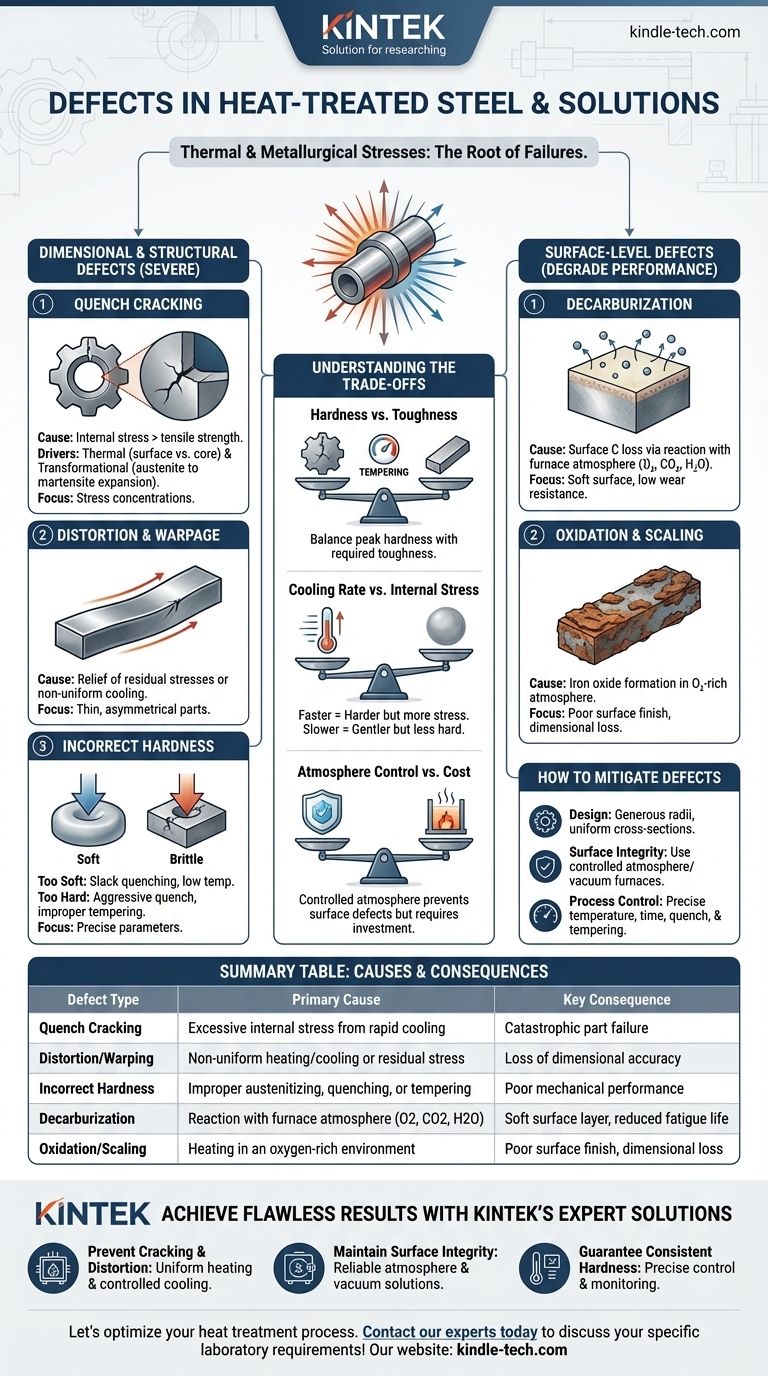
Les défauts dans l'acier traité thermiquement sont principalement causés par les énormes contraintes thermiques et métallurgiques introduites pendant le chauffage et le refroidissement rapide. Les défauts les plus courants sont les fissures, la distorsion (gauchissement), les changements de surface indésirables tels que la décarburation et la calamine, et l'incapacité d'atteindre la dureté ou la microstructure cible. Ces défaillances ne sont pas aléatoires mais sont des conséquences directes de paramètres de processus mal contrôlés.
Les défauts de traitement thermique sont des résultats prévisibles des contraintes thermiques, des transformations de phase et des réactions chimiques atmosphériques. Leur prévention repose sur le contrôle rigoureux du taux de changement de température, de l'atmosphère du four et de la géométrie de la pièce dès la phase de conception.

Défaillances dimensionnelles et structurelles
Les défauts les plus graves compromettent l'intégrité mécanique et la précision dimensionnelle du composant, le rendant souvent inutilisable.
Fissuration par trempe
La fissuration par trempe est le défaut de traitement thermique le plus critique. Elle se produit lorsque les contraintes internes dues à la trempe dépassent la résistance à la traction ultime du matériau.
Ceci est entraîné par deux forces principales : la contrainte thermique due au refroidissement de la surface beaucoup plus rapide que le cœur, et la contrainte transformationnelle due à l'expansion qui se produit lorsque l'austénite se transforme en martensite fragile.
Les fissures proviennent généralement des points de concentration de contraintes tels que les angles vifs, les rainures de clavette ou les changements brusques de la section transversale de la pièce.
Distorsion et gauchissement
La distorsion est un changement irréversible de la taille ou de la forme d'un composant qui se produit pendant le traitement thermique.
Ceci est souvent causé par la libération des contraintes résiduelles imposées lors des étapes de fabrication antérieures (comme l'usinage) ou par un chauffage et un refroidissement non uniformes. Les pièces minces, longues ou asymétriques sont particulièrement sujettes au gauchissement.
Dureté incorrecte
Atteindre la dureté correcte est souvent l'objectif principal, et l'échec à cet égard peut être dû à plusieurs facteurs.
Une pièce trop molle peut résulter d'une température ou d'un temps d'austénitisation insuffisant, ou d'une trempe trop lente pour la trempabilité de l'acier (appelée trempe incomplète). À l'inverse, une pièce trop dure et fragile est souvent le résultat d'une trempe trop agressive ou, plus communément, d'une étape de revenu inappropriée ou manquée après la trempe.
Défauts de surface
Ces défauts dégradent la surface de l'acier, compromettant ses performances dans les applications nécessitant une résistance élevée à l'usure ou à la fatigue.
Décarburation
La décarburation est la perte de carbone à la surface de l'acier. C'est un problème important car le carbone est l'élément principal responsable de la dureté de l'acier.
Elle est causée par une réaction chimique entre l'acier et l'atmosphère du four (oxygène, dioxyde de carbone, vapeur d'eau) à haute température. Le résultat est une couche superficielle molle et faible qui réduit considérablement la résistance à l'usure et la durée de vie en fatigue.
Oxydation et calamine
L'oxydation est la formation d'une couche d'oxyde de fer (calamine) à la surface du composant lorsqu'il est chauffé dans une atmosphère riche en oxygène.
Cette calamine entraîne une mauvaise finition de surface et une perte de précision dimensionnelle. Elle peut également isoler la pièce, conduisant à une trempe non uniforme et masquant potentiellement des défauts sous-jacents plus graves comme les fissures de trempe.
Comprendre les compromis
La sélection d'un processus de traitement thermique implique toujours de mettre en balance des facteurs concurrents. Comprendre ces compromis est essentiel pour prévenir les défauts.
Dureté contre ténacité
Le compromis fondamental dans le traitement thermique est que les processus qui créent une dureté extrême, comme la trempe, créent également une microstructure fragile (martensite non revenue).
Le revenu est l'étape post-trempe essentielle qui réduit cette fragilité et cette contrainte interne, conférant de la ténacité. Cependant, ce processus réduit également la dureté maximale. L'art consiste à trouver l'équilibre précis requis pour l'application.
Vitesse de refroidissement contre contrainte interne
Une vitesse de refroidissement plus rapide est plus efficace pour atteindre la dureté complète, en particulier dans les aciers à faible teneur en alliage.
Cependant, une trempe rapide (par exemple, en utilisant de l'eau ou de la saumure) génère d'immenses gradients thermiques et des contraintes internes, augmentant considérablement le risque de distorsion et de fissuration. Une trempe plus lente (par exemple, en utilisant de l'huile ou du gaz) est plus douce mais peut ne pas atteindre la dureté maximale.
Contrôle de l'atmosphère contre coût
L'utilisation d'une atmosphère contrôlée (comme le vide, l'azote ou l'argon) empêche complètement la décarburation et l'oxydation, produisant une pièce propre et brillante.
Ces processus, cependant, nécessitent des équipements plus sophistiqués et plus coûteux par rapport au chauffage dans un four à air libre. Le coût doit être justifié par les exigences de surface du composant.
Comment atténuer les défauts de traitement thermique
La prévention des défauts nécessite une approche systématique axée sur la conception, la sélection des matériaux et un contrôle précis du processus.
- Si votre objectif principal est de prévenir les fissures et la distorsion : Concevez des pièces avec des rayons généreux et des sections transversales uniformes, et sélectionnez un milieu de trempe moins sévère adapté à la trempabilité de l'acier.
- Si votre objectif principal est de maintenir l'intégrité de la surface : Utilisez des fours à atmosphère contrôlée (par exemple, sous vide, gaz inerte) ou des revêtements protecteurs pour prévenir la décarburation et la formation de calamine.
- Si votre objectif principal est d'obtenir une dureté constante : Assurez un contrôle précis de la température d'austénitisation, du temps de maintien et de l'agitation de la trempe, et suivez toujours par un cycle de revenu approprié.
Un traitement thermique réussi est un processus d'ingénierie contrôlé où la prévoyance dans la conception et la précision dans l'exécution déterminent la qualité finale du composant.
Tableau récapitulatif :
| Type de défaut | Cause principale | Conséquence clé |
|---|---|---|
| Fissure par trempe | Contrainte interne excessive due au refroidissement rapide | Défaillance catastrophique de la pièce |
| Distorsion/Gauchissement | Chauffage/refroidissement non uniforme ou contrainte résiduelle | Perte de précision dimensionnelle |
| Dureté incorrecte | Austénitisation, trempe ou revenu inappropriés | Mauvaise performance mécanique |
| Décarburation | Réaction avec l'atmosphère du four (O2, CO2, H2O) | Couche superficielle molle, durée de vie en fatigue réduite |
| Oxydation/Calamine | Chauffage dans un environnement riche en oxygène | Mauvaise finition de surface, perte dimensionnelle |
Obtenez des résultats impeccables avec les solutions expertes de KINTEK
Éliminez les défauts coûteux de traitement thermique et assurez-vous que vos composants en acier répondent aux normes les plus élevées en matière de dureté, de durabilité et de précision dimensionnelle. KINTEK se spécialise dans les équipements de laboratoire et les consommables haut de gamme, fournissant les fours, les systèmes de contrôle d'atmosphère et le support expert dont votre laboratoire a besoin pour perfectionner son traitement thermique.
Nous vous aidons à :
- Prévenir les fissures et la distorsion : Avec des équipements conçus pour un chauffage uniforme et un refroidissement contrôlé.
- Maintenir l'intégrité de la surface : Grâce à des solutions de fours fiables à atmosphère contrôlée et sous vide.
- Garantir une dureté constante : Avec un contrôle précis de la température et des outils de surveillance.
Optimisons votre processus de traitement thermique. Contactez nos experts dès aujourd'hui pour discuter de vos besoins spécifiques en laboratoire !
Guide Visuel
Produits associés
- Four de traitement thermique sous vide avec revêtement en fibre céramique
- Four de traitement thermique et de frittage sous vide de tungstène à 2200 ℃
- Four de traitement thermique sous vide et four de fusion par induction à lévitation
- Four de traitement thermique sous vide au molybdène
- Four de frittage et de brasage sous vide pour traitement thermique
Les gens demandent aussi
- Quels sont les avantages du traitement thermique sous vide ? Obtenez une précision et une propreté supérieures pour les composants critiques
- Comment le refroidissement à l'argon et à l'azote se compare-t-il dans les fours sous vide ? Un guide pour une trempe plus rapide et moins chère
- Quels matériaux sont utilisés dans un four sous vide ? Un guide sur les matériaux de zone chaude et les métaux traités
- Comment aspirer une fournaise ? Un guide étape par étape pour un entretien DIY sûr
- Quelle est l'épaisseur standard du placage ? Optimiser la durabilité, la corrosion et le coût



















