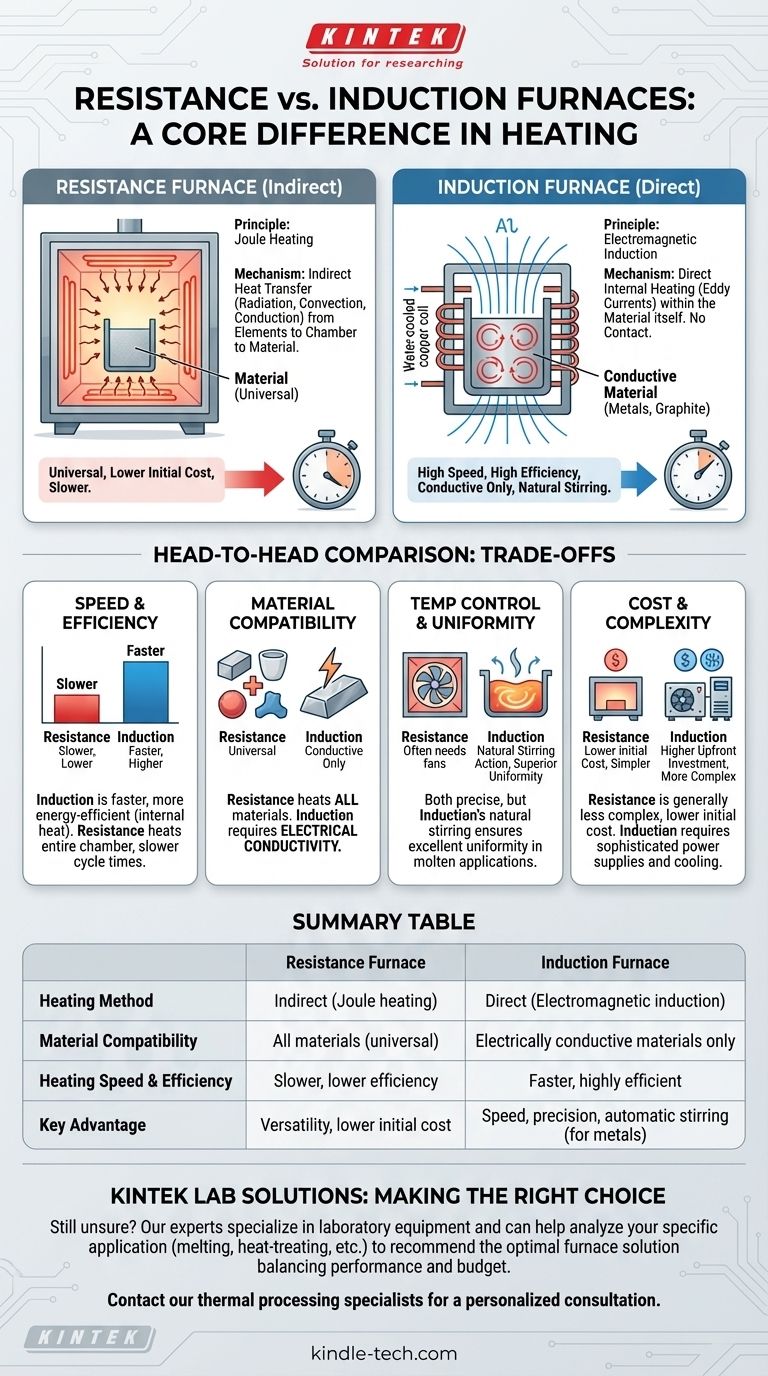
La différence fondamentale entre un four à résistance et un four à induction réside dans leur méthode de chauffage. Un four à résistance utilise des éléments chauffants qui deviennent chauds et transfèrent la chaleur au matériau indirectement, un peu comme un four conventionnel. Un four à induction, en revanche, utilise un champ électromagnétique pour générer de la chaleur directement à l'intérieur du matériau conducteur lui-même, sans contact physique.
La décision essentielle entre ces deux technologies se résume à un compromis entre polyvalence et efficacité. Les fours à résistance sont l'outil universel pour chauffer n'importe quel matériau, tandis que les fours à induction sont les spécialistes rapides et très efficaces pour les matériaux conducteurs comme le métal.

Comment fonctionne un four à résistance
Un four à résistance est le type de four électrique le plus courant et le plus simple, fonctionnant sur un principe familier à quiconque a utilisé un grille-pain ou une cuisinière électrique.
Le principe : Chauffage Joule
Le mécanisme est basé sur la résistance électrique. Un courant électrique élevé est passé à travers un élément chauffant spécialement conçu, fait d'un matériau à haute résistance.
Cette résistance au flux d'électricité fait que l'élément devient extrêmement chaud, un effet connu sous le nom de chauffage Joule.
Le mécanisme : Transfert de chaleur indirect
La chaleur intense de ces éléments est ensuite transférée au matériau à l'intérieur du four. Cela se produit par une combinaison de rayonnement, de convection et de conduction.
Essentiellement, le four chauffe l'atmosphère et les parois de la chambre, ce qui à son tour chauffe le matériau cible. C'est un processus de chauffage indirect.
Caractéristiques clés
Les fours à résistance sont connus pour leur polyvalence, car ils peuvent chauffer tout type de matériau, qu'il soit conducteur ou non. Ils sont généralement de conception plus simple et moins chers à l'achat.
Comment fonctionne un four à induction
Le chauffage par induction est une méthode plus avancée, ciblée et efficace qui modifie fondamentalement la manière dont l'énergie thermique est délivrée à un matériau.
Le principe : Induction électromagnétique
Un four à induction utilise une bobine puissante pour générer un champ magnétique rapidement alternatif. Lorsqu'un matériau conducteur (comme l'acier ou le graphite) est placé dans ce champ, le champ induit des courants électriques à l'intérieur du matériau lui-même.
Ces petits courants circulaires sont connus sous le nom de courants de Foucault.
Le mécanisme : Chauffage interne direct
La résistance naturelle du matériau à ces courants de Foucault génère une chaleur précise et rapide de l'intérieur vers l'extérieur. Aucun élément chauffant externe n'est nécessaire.
La chaleur est générée directement à l'intérieur de la pièce, ce qui rend le processus extrêmement rapide et efficace, car très peu d'énergie est gaspillée à chauffer l'espace environnant.
Caractéristiques clés
Un avantage unique du chauffage par induction pour les métaux en fusion est l'action d'agitation naturelle causée par les champs magnétiques. Cela assure une excellente uniformité de la température et un bon mélange des alliages sans agitateurs mécaniques.
Comprendre les compromis : Une comparaison directe
Le choix du bon four nécessite de comprendre les avantages et les limites distincts inhérents à chaque méthode de chauffage.
Vitesse de chauffage et efficacité
Les fours à induction sont significativement plus rapides et plus économes en énergie. Parce que la chaleur est générée en interne, la température cible est atteinte en une fraction du temps, et moins d'énergie est perdue dans l'environnement.
Les fours à résistance doivent d'abord chauffer les éléments et toute la chambre du four, ce qui entraîne des temps de cycle plus lents et une efficacité globale plus faible.
Compatibilité des matériaux
Les fours à résistance sont universels. Ils peuvent chauffer des métaux, des céramiques, des polymères et des composites sans problème, car leur fonctionnement ne dépend pas des propriétés électriques du matériau.
Les fours à induction sont des spécialistes. Ils sont très efficaces mais ne peuvent chauffer que des matériaux électriquement conducteurs.
Contrôle de la température et uniformité
Les deux types peuvent atteindre des niveaux élevés de contrôle de la température. Cependant, l'effet d'agitation naturelle dans un four à induction offre une uniformité thermique supérieure dans les applications de métaux en fusion.
Dans les fours à résistance, l'obtention d'une grande uniformité nécessite souvent des ventilateurs pour faire circuler l'atmosphère, ce qui ajoute de la complexité.
Coût et complexité
Les fours à résistance sont généralement moins complexes et ont un coût initial plus faible. Leur maintenance est souvent plus simple et moins chère sur leur durée de vie.
Les fours à induction sont des systèmes plus complexes, nécessitant des alimentations électriques sophistiquées et des systèmes de refroidissement, ce qui entraîne un investissement initial plus élevé.
Faire le bon choix pour votre application
Votre décision finale doit être entièrement guidée par votre matériau spécifique, les exigences de votre processus et votre budget.
- Si votre objectif principal est la polyvalence et un coût initial plus faible : Un four à résistance est le choix supérieur, servant de cheval de bataille fiable pour une grande variété de matériaux et d'applications.
- Si votre objectif principal est la vitesse, l'efficacité énergétique et le traitement des métaux conducteurs : Un four à induction offre des performances inégalées, en particulier pour la fusion, le brasage ou le traitement thermique à grande vitesse.
- Si vous travaillez avec des matériaux non conducteurs comme les céramiques : Un four à résistance est votre seule option viable.
- Si vous avez besoin d'une agitation automatique d'un bain de métal en fusion : L'agitation électromagnétique inhérente à un four à induction est un avantage opérationnel majeur.
Comprendre cette différence fondamentale dans le mécanisme de chauffage est la clé pour sélectionner l'outil le plus efficace pour votre tâche de traitement thermique spécifique.
Tableau récapitulatif :
| Caractéristique | Four à résistance | Four à induction |
|---|---|---|
| Méthode de chauffage | Indirect (Chauffage Joule) | Direct (Induction électromagnétique) |
| Compatibilité des matériaux | Tous matériaux (universel) | Matériaux électriquement conducteurs uniquement |
| Vitesse et efficacité de chauffage | Plus lent, moins efficace | Plus rapide, très efficace |
| Avantage clé | Polyvalence, coût initial plus faible | Vitesse, précision, agitation automatique (pour les métaux) |
Vous ne savez toujours pas quel four convient le mieux aux matériaux et processus spécifiques de votre laboratoire ?
KINTEK est spécialisé dans les équipements et consommables de laboratoire. Nos experts peuvent vous aider à analyser les exigences de votre application — que vous fondiez des métaux, traitiez thermiquement des alliages ou traitiez des céramiques — afin de vous recommander la solution de four optimale qui équilibre performance, efficacité et budget.
Contactez nos spécialistes du traitement thermique dès aujourd'hui pour une consultation personnalisée et découvrez comment le bon four peut améliorer la productivité et les résultats de votre laboratoire.
Guide Visuel
Produits associés
- Four à tube de laboratoire à haute température de 1400℃ avec tube en alumine
- Four à tube de laboratoire à haute température de 1700℃ avec tube en alumine
- Four de laboratoire tubulaire vertical
- Four tubulaire de traitement thermique rapide (RTP) de laboratoire
- Four à moufle de 1800℃ pour laboratoire
Les gens demandent aussi
- Pourquoi un four à tube de quartz est-il utilisé dans l'oxydation thermique des revêtements de MnCr2O4 ? Débloquez une oxydation sélective précise
- Comment nettoyer un four tubulaire ? Un guide étape par étape pour un entretien sûr et efficace
- Quelles précautions faut-il prendre lors de l'utilisation d'un four tubulaire ? Assurez un traitement à haute température sûr et efficace
- Quels matériaux sont utilisés pour les tubes dans les fours tubulaires ? Un guide pour choisir le bon tube pour votre processus
- Comment un réacteur à tube de quartz et un four à atmosphère collaborent-ils dans la pyrolyse de Co@NC ? Maîtrisez la synthèse de précision



















